7. User Information
7.5 Safe transport of Portable Liquid Vessels (PLV)
Our PLVs are designed to withstand normal handling and vibration in transit. Nevertheless, there are various precautions that need to be adhered to for safe handling of our PLVs.
Usage and Storage
- Store and use in ventilated areas.
- Close all valves when PLV is not in use.
- Do not apply oil or grease on any fittings on the vessel or its connecting pipework or hoses.
Transport
- Keep the vessel upright during use and transportation.
- Do not manoeuvre the trolley on uneven surfaces as it may topple and injure the user.
- Never remove the vessel from its trolley frame.
- Avoid rough handling, dropping or striking. As there is a vacuum between the outer and inner vessel, a blow on the outer vessel can render the PLV unserviceable.
Handling Cryogenic Liquids
- Please take special care to avoid contact with liquid or any uninsulated parts of the vessel as it can cause severe cold burns.
- Protective clothing (leather gloves, faces-shield, aprons, etc) should be worn.
Maintenance
- Do not attempt to carry out maintenance of the PLV on your own.
- Contact Air Liquide in case of any suspected defect or malfunction.
- Do not change indentation lettering or labeling on the PLV or fittings.
7. User Information
7.5 Operating Instructions of Portable Liquid Vessel
Gas or liquid can automatically be disbanded at pre-set pressure by means of a built-in vaporiser and pressure regulator.

Nomenclature
- Liquid Use Valve
- Pressure Building Regulator
- Pressure Building Valve
- Vent Valve
- Bursting Disc
- Pressure Gauge
- Pressure Relief Valve
- Gas Use Valve
- Liquid Level Indicator
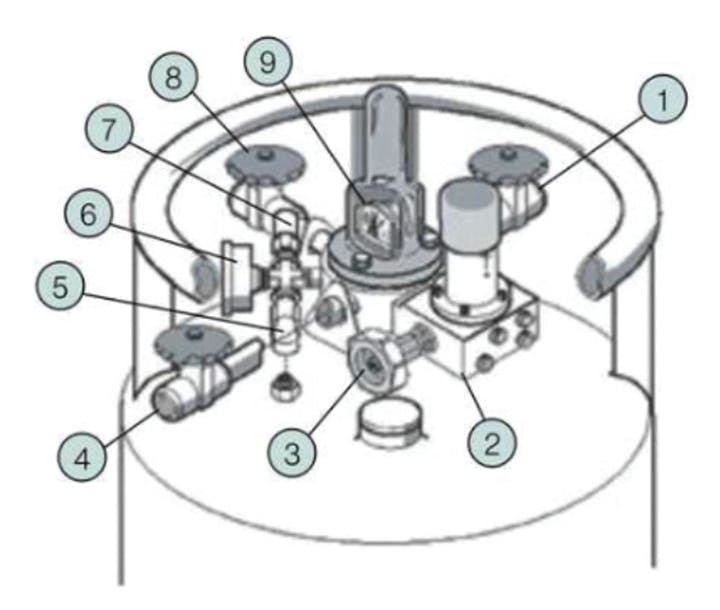
For Gas Withdrawal
- Connect adaptor and regulator onto the Gas Use Valve (8) outlet.
- Open Pressure Building Valve (3) and also the Gas Use Valve (8). The pressure will reach the preset operating pressure and maintain it.
- Do not attempt to adjust the Pressure Building Regulator (2) as it has been factory-set to achieve correct operation.
- When gas is no longer required, first shut the Pressure Building Valve (3) and then shut the Gas Use Valve (8).
- If the PLV is kept unused over an extended period or if the Pressure Building Valve (3) is left open after use there is a possibility that the Pressure Relief Valve (7) will release the excessive pressure. This is a normal phenomenon. The pressure can also be reduced by slightly opening the Vent Valve (4) in a well-ventilated area.
- Formation of ice on the outer shell is expected in case the draw-off rate of gas is excessive under prolonged usage.
For Liquid Withdrawal
- Connect one end of the stainless steel liquid transfer hose to the Liquid Use Valve (1) outlet on the PLV and the other end of the hose to the user’s equipment.
- Liquid withdrawal from a liquid cylinder is normally performed at low pressure to minimize flash vaporisation losses. Therefore the Pressure Valve Building (3) is normally kept close during liquid transfer. If pressure exceeds the user’s recruitment, the excessive pressure can be released to the Vent Valve (4).
- Higher service pressure can be obtained by opening the Pressure Valve Building (3) up to the desired pressure and then shutting it.
- Keep the transfer hose as short as possible to minimise gas loss.
- Lines between the two valves must be equipped with a safety release valve.
- When filling an open neck dewar, fit a phase separator on the end of the transfer hose to minimise flash-off and spillage.
